Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a Gram-negative, spiral-shaped bacterium that mainly parasitizes the human gastric mucosa and is an important pathogen that causes digestive system diseases such as chronic gastritis, gastric ulcers, and gastric cancer. Helicobacter pylori can be divided into several types based on their different characteristics and pathogenicity. This article will introduce these types and their related characteristics in detail.
1. Classification based on pathogenicity
Helicobacter pylori can be divided into two categories according to its pathogenicity: pathogenic and non-pathogenic.
1.1 Pathogenic Helicobacter pylori
Pathogenic Helicobacter pylori refers to strains that can cause gastrointestinal diseases. Such strains are usually highly pathogenic and can cause serious diseases such as chronic gastritis, gastric ulcers, and gastric cancer. The characteristics of pathogenic strains include:
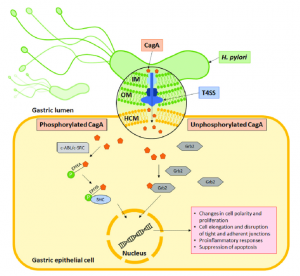
- CagA-positive strains: CagA (cytotoxicity-associated gene A) is a virulence factor closely related to gastric cancer. After CagA-positive strains are injected into host cells, they can change the signal transduction pathways of host cells, thereby promoting cell proliferation and apoptosis, and increasing the risk of cancer.
- VacA positive strains: VacA (gastric toxin A) is a toxin that can cause cell damage and apoptosis. VacA positive strains can cause gastritis and ulcers by destroying the gastric mucosal barrier.
1.2 Non-pathogenic Helicobacter pylori
Non-pathogenic Helicobacter pylori usually does not cause obvious clinical symptoms and may exist in the stomach of some healthy individuals. The pathogenicity of this type of strain is low, which may be related to environmental factors such as the host’s immune status. Although non-pathogenic strains usually do not cause disease, in some cases, they may work together with other pathogens to cause gastrointestinal diseases.
2. Classification based on genomic features
The genomic characteristics of Helicobacter pylori can also be used to classify it. Different strains have different genomes, and these differences may affect their pathogenicity and drug resistance.
2.1 Genomic diversity
The Helicobacter pylori genome is highly diverse, and the genomes of strains isolated from different regions and populations may differ significantly. This diversity enables Helicobacter pylori to adapt to different host environments, thus affecting its pathogenicity.
2.2 Drug resistance
With the widespread use of antibiotics, the drug resistance of Helicobacter pylori is becoming increasingly serious. Some strains may develop resistance to commonly used antibiotics (such as clarithromycin, amoxicillin, etc.), making treatment more complicated. Based on the characteristics of drug resistance, Helicobacter pylori can be divided into sensitive and resistant types.
3. Classification by distribution area
Different types of Helicobacter pylori are distributed differently around the world. Depending on the geographical region, Helicobacter pylori can be divided into the following types:
3.1 Asian Type
The infection rate of Helicobacter pylori is high in Asia, especially in East Asia and Southeast Asia. Studies have shown that Asian strains are usually more pathogenic and are closely related to the occurrence of gastric cancer.
3.2 European style
The infection rate of Helicobacter pylori in Europe is low and its pathogenicity is weak. Studies have found that the CagA positivity rate of European strains is low, leading to a lower risk of gastric cancer.
3.3 African Type
The characteristics of African Helicobacter pylori have not yet been fully elucidated, but studies have shown that strains in the African region may have unique genomic characteristics and pathogenic mechanisms.
4. Conclusion
Helicobacter pylori is a highly diverse pathogenic bacterium. Different types show significant differences in pathogenicity, genomic characteristics, and geographical distribution. Understanding the characteristics of these types is of great significance for clinical diagnosis and treatment. With the continuous deepening of research on Helicobacter pylori, more types and characteristics may be discovered in the future, providing new ideas and methods for the prevention and treatment of related diseases.
A note from Xiamen Baysen Medical
We baysen Medical always focus on diagnostic techniques to imporve the quality of life, We already develop HP-ab Test kit , HP-ag Test kit and Hp-ab-s test kit for screening of Helicobacter Pylori
Post time: Dec-26-2024