What is Diabetes ?
Diabetes is a metabolic disease characterized by abnormally high levels of blood glucose (glucose in the blood). Normally, the pancreas secretes insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose, thereby maintaining stable blood glucose levels. However, in people with diabetes, insulin is not secreted enough or cells do not respond well to insulin, resulting in inefficient use of blood glucose.
What are the types of diabetes?
There are many types of diabetes, which are mainly divided into the following categories:
1)Type 1 Diabetes: This type of diabetes usually occurs in children or young adults and is characterized by the body’s immune system attacking and destroying the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, people with type 1 diabetes produce almost no insulin and require lifelong insulin therapy.
2)Type 2 Diabetes: This is the most common type of diabetes and is often associated with obesity, lack of exercise, and a poor diet. People with type 2 diabetes either have a body that doesn’t produce enough insulin or their cells become resistant to insulin. It can usually be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin therapy.
3)Gestational diabetes: This disease occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after delivery. However, it increases the risk of both the mother and the child developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
4)Other specific types of diabetes: This category includes diabetes caused by genetic disorders, hormone disorders, certain medications, or other medical conditions. These types are less common and may require special treatments.
Understanding these types can help determine appropriate treatment and management strategies for people with diabetes
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Symptoms of diabetes vary from person to person and depending on the type of diabetes you have, but common symptoms include:
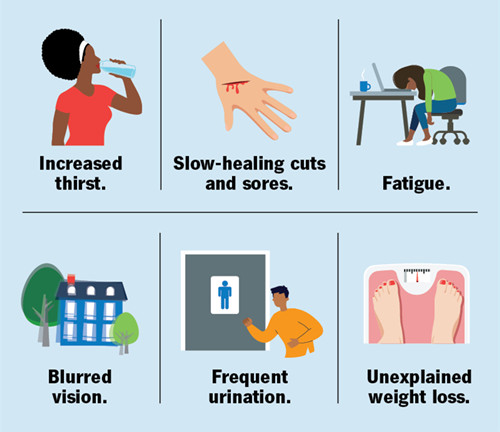
Frequent urination: High blood sugar can cause the kidneys to excrete excess glucose, which in turn causes frequent urination.
Thirst: Due to frequent urination, the body loses a lot of water, leading to increased thirst.
Hunger: Even after eating, blood sugar levels may still be high and cells cannot use glucose effectively, resulting in continued hunger.
Fatigue: Because the body cannot effectively use glucose, patients may feel tired and weak.
Blurred vision: High blood sugar may cause the lens of the eye to swell, which can affect vision.
Slow wound healing: Diabetes may affect the body’s healing ability, causing wounds and infections to heal slowly
Skin problems: People with diabetes may be more susceptible to skin infections and other skin problems.
Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet: Long-term high blood sugar levels may cause nerve damage, resulting in numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands and feet.
If you experience the above symptoms, it is recommended to seek medical attention for examination and diagnosis in a timely manner. Early detection and management of diabetes can effectively reduce the risk of complications.
How is diabetes diagnosed ?
Diabetes can be diagnosed in a variety of ways, mainly involving blood tests to measure blood sugar levels. The most common tests include:
1. Fasting Blood Glucose (FPG) Test: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast (at least 8 hours without eating). A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher indicates diabetes.
2.Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): This test requires fasting overnight and then drinking a sugar solution. After drinking the solution, blood sugar levels are checked at intervals. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher two hours after drinking the solution indicates diabetes.
3.HbA1c test: This test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 to 3 months. Hb A1c level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes.
4. Random plasma glucose test: This test measures blood sugar at any time of the day, regardless of when the patient last ate. Blood sugar levels of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher indicate diabetes, especially if accompanied by symptoms of high blood sugar, such as thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
If either test suggests diabetes, a healthcare provider may repeat the test on another day to confirm the diagnosis. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for the correct testing and interpretation of results.
How is diabetes managed ?
1. Monitoring blood Glucose levels
1)Self-monitoring: Check your blood sugar levels regularly using a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to understand how food, activity, and medications affect your blood sugar.
2)HbA1C test: Regular testing (usually every 3-6 months) to assess your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
2.Insulin Therapy:
For type 1 diabetes and some cases of type 2 diabetes, you may need to take insulin injections or use an insulin pump.
3.Regular physical examination
Regular Visits: Make regular appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor diabetes management, adjust your treatment plan, and screen for complications.
Complication screening: Regular checks for potential complications, such as eye exams, foot exams, and kidney function tests.
4.Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption
Quit smoking: Quit smoking to reduce the risk of complications.
Alcohol in moderation: Drink alcohol in moderation and understand its effects on blood sugar.
5.Diet and Nutrition
1) Balanced Diet: Eat a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while limiting processed foods, sugar, and refined carbohydrates.
2) Carb Counting: Understand your carbohydrate intake to effectively manage blood sugar levels.
Meal Plan: Regular meal times and portion control help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Physical activity
3) Exercise Regularly: Engage in regular physical activity (e.g., walking, biking, swimming) to improve insulin sensitivity and help manage weight.
4) Incorporate movement: Find ways to stay active throughout the day, such as taking the stairs or taking a walk during breaks.
Effective diabetes management varies from person to person and may need to be adjusted over time. People with diabetes must work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized management plan.
A note from Xiamen Baysen Medical
We baysen Medical always focus on diagnostic techniques to imporve the quality of life, We already develop Hba1c test kit , Insulin test kit and C-peptide test kit for Diabetes disease.
Post time: Dec-09-2024