Fecal Occult Blood (FOB) testing is a critical diagnostic tool used to detect hidden (occult) blood in stool samples, which may indicate gastrointestinal bleeding. This non-invasive test plays a vital role in the early detection of colorectal cancer, polyps, and other gastrointestinal disorders, making it an essential component of preventive healthcare.
What is FOB Testing?
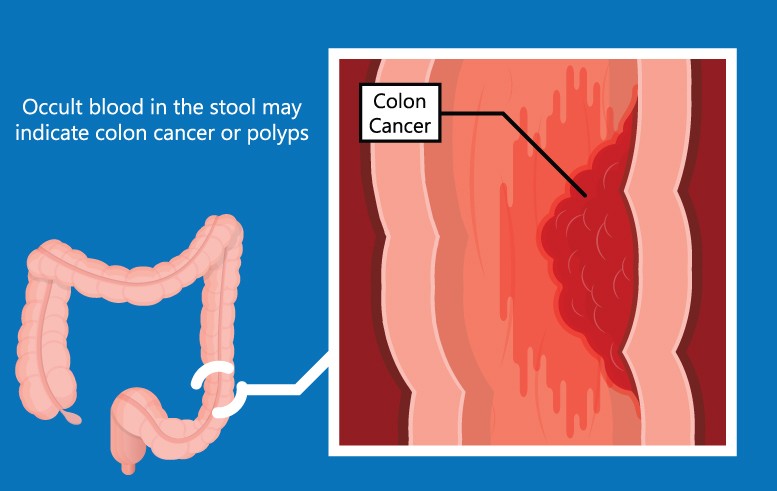
FOB testing is designed to identify small amounts of blood in the stool that are not visible to the naked eye. The presence of occult blood can be a sign of various conditions, including colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), ulcers, or hemorrhoids. The test works by detecting the peroxidase-like activity of hemoglobin or globin proteins in the stool, which are indicative of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
Types of FOB Tests
There are two main types of FOB tests: the guaiac-based fecal occult blood test (gFOBT) and the fecal immunochemical test (FIT).
1. Guaiac-based FOBT (gFOBT): This traditional method uses a chemical reaction to detect heme, a component of hemoglobin. Patients typically collect stool samples from three consecutive bowel movements, which are then applied to specially treated cards. The cards are analyzed in a laboratory, where a chemical developer is added to reveal any hidden blood.
2. Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT):FIT is a more advanced and specific method that uses antibodies to detect human hemoglobin. Unlike gFOBT, FIT does not require dietary restrictions and is less likely to produce false positives. It is also more sensitive to lower gastrointestinal bleeding, making it a preferred choice for colorectal cancer screening.
Clinical Significance
FOB testing is particularly valuable in colorectal cancer screening programs. Colorectal cancer often develops from precancerous polyps, which can bleed intermittently. Detecting this blood early through FOB testing can lead to timely diagnostic follow-ups, such as colonoscopy, and significantly improve patient outcomes. The American Cancer Society recommends regular FOB testing for adults aged 45 and older as part of routine cancer screening.
Limitations and Considerations
While FOB testing is a powerful tool, it is not without limitations. False positives can occur due to dietary factors (e.g., red meat, certain vegetables) or medications (e.g., aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Conversely, false negatives may result from intermittent bleeding or the degradation of hemoglobin during sample storage. Therefore, FOB testing should be part of a comprehensive screening strategy, complemented by other diagnostic methods when necessary.
Conclusion
FOB testing is a simple, non-invasive, and cost-effective method for detecting gastrointestinal bleeding, particularly in the context of colorectal cancer screening. By enabling early detection of potentially life-threatening conditions, FOB testing plays a crucial role in reducing morbidity and mortality associated with gastrointestinal diseases. As healthcare continues to emphasize preventive care, FOB testing remains an indispensable tool in the clinician’s arsenal.
Post time: Mar-03-2025