Introduction
Refractory mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (RMPP) is a lung infection caused by mycoplasma, usually manifested by persistent cough, fever and dyspnea. Although most patients recover after receiving conventional antibiotic treatment, some patients develop refractory symptoms, which poses a challenge to clinical treatment. In recent years, researchers have begun to focus on the role of biomarkers in refractory Mycoplasma pneumonia, in order to improve the prognosis of patients through early diagnosis and personalized treatment.
Clinical features of RMPP
Refractory mycoplasma pneumonia usually occurs in children and adolescents, with diverse clinical manifestations, including persistent cough, low-grade fever, fatigue, etc. Some patients may experience severe symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath. Due to the hidden nature and diversity of mycoplasma infection, routine imaging examinations and laboratory tests are often difficult to diagnose, causing some patients to seek medical treatment repeatedly during treatment, increasing the medical burden.
Biomarkers Relevent for Prdicting RMPP
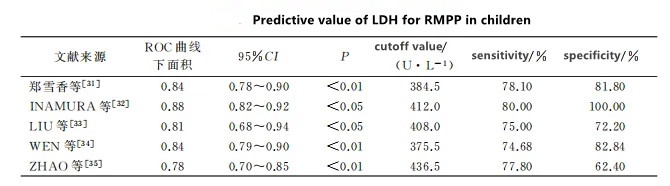
1.LDH is an oxidoreductase that is widely present in the cytoplasm of human tissue cells and participates in anaerobic sugar metabolism. There are 5 subtypes: LDH1, LDH2, LDH3, LDH4 and LDH5. LDH3 is most abundant in lung tissue. Tissue damage during inflammation can often be monitored by detecting LDH levels in serum. Many studies have shown that LDH is significantly increased during RMPP and is one of the more reliable predictors of RMPP. Its cut-off value range is 375.5-436.5 U·L-1 (Table 1). Zheng Xuexiang et al. used 384.5U·L-1 as the cut-off value to conduct multi-factor logistic regression analysis, showing that LDH is an independent risk factor for RMPP, with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.006. INAMURA and other studies found that LDH ≥ 410 U·L-1 may be an indicator for recommending initial treatment with corticosteroids. Research by LIU et al. found that the joint prediction of its isoenzymes (LDH4+LDH5) may also be a good predictor of predicting RMPP and starting corticosteroid treatment. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.829, when the cutoff value was 109.4 U·L-1 , the predicted specificity is 87% and the sensitivity is 75%. However, the sample size of this study was small (16 cases in the RMPP group), and relevant studies with a larger sample size and more direct evidence are needed to explain why LDH5 and LDH4 are higher than LDH3 in RMPP.
2. SF is a recognized dual indicator of the human body’s important iron storage protein and inflammatory response. A significantly elevated SF level reflects a disorder in iron metabolism and is a signal for judging the severity and prognosis of the disease. In the early stages of infection, activated macrophages are stimulated to synthesize and release cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby stimulating the synthesis of ferritin. High levels of SF exert an immunosuppressive effect by inhibiting lymphocyte proliferation. In the respiratory system, elevated SF levels can reflect the degree of lung inflammation and tissue damage. Studies by CHOI et al. have shown that SF can be used as one of the early predictive biomarkers for RMPP in children. When the SF cutoff value is 230pg·mL-1, the sensitivity and specificity for predicting RMPP are both 67%. Studies by WEN et al. have shown that SF is associated with the severity of RMPP in children and may be an indicator for starting corticosteroid treatment, with an AUC of 0.90. When the SF cutoff value is 329ng·mL-1, multivariate logistic regression analysis shows that SF is an independent risk factor for RMPP, with an OR value of 1.00. The low cost of SF and its wide application in hospitals at all levels can increase its applicability and practicality. However, more research is still needed to determine the cutoff range suitable for clinical work.
3.C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute-phase protein synthesized by hepatocytes and is widely used as a non-specific infection biomarker of systemic inflammatory response. Eliminate pathogenic microorganisms and damaged tissue cells by activating complement and enhancing phagocytosis of phagocytes. In recent years, some studies have shown that the CRP level of the RMPP group is statistically significantly higher than that of the GMPP group and can be used as one of the effective indicators for predicting RMPP. WEN et al.’s study showed that its AUC was 0.81. When the cut-off value of CRP was 43 mg·L-1, the prediction specificity was 82.73% and the sensitivity was 62.03%. Logistic regression analysis was performed on it, showing that CRP is an independent risk factor for RMPP. , the OR value is 1.02.0
4. D-dimer is the simplest hydrolysis product of fibrin and is an independent predictor of thrombotic events. Reports of thrombosis in MPP are not uncommon in recent years. Its clinical value in predicting the severity and prognosis of pneumonia is gradually being recognized and can be used to assess the severity of MPP. Direct infection and abnormal immune response of MP lead to systemic inflammation, followed by vascular endothelial damage, subcutaneous collagen exposure and vasoconstriction, which disrupt the balance of blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems, leading to a hypercoagulable state and a higher level of D-dimer. In particular, D-dimer>1.11mg·L-1 helps indicate RMPP with thrombosis. Therefore, some scholars have studied the role of D-dimer in predicting RMPP infection and found that it can effectively predict the occurrence of RMPP with an AUC of 0.87. When D-dimer ≥2.1mg·L-1, this cutoff value has a prediction specificity of 81% and a sensitivity of 79%. Huang et al. studied 124 children with RMPP and found that multivariate logistic regression analysis of D-dimer with a cutoff value of 0.738 mg·L-1 showed that D-dimer was an independent risk factor for RMPP, with an OR value of 1.002.
In summary,The Level change of LDH,SF,CRP,D-dimer,IL-6 have Sense to Prdictin RMPP .
We baysen medical is always focus on diagnostic technique to improve the quality of life.
Post time: Dec-16-2024