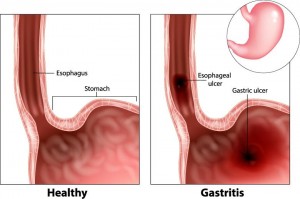
Biomarkers of chronic atrophic gastritis include:
1. Autoantibodies of gastric mucosal cells: Patients with chronic atrophic gastritis may produce anti-parietal cell antibodies and anti-intrinsic factor antibodies.
2. Serum pepsinogen I (PGI) and pepsinogen II (PGII): PGI and PGII are proteases secreted by gastric mucosal cells, and their concentrations can reflect the functional status of the gastric mucosa.
3. Serum pepsinogen I/II ratio: The PGI/PGII ratio can be used as an indicator for the diagnosis of chronic atrophic gastritis and the evaluation of disease activity.
4. Serum pepsinogen I and II concentrations: Decreased concentrations of PGI and PGII may indicate the presence of chronic atrophic gastritis.
These biomarkers can be assessed through serum testing and can aid in the diagnosis of chronic atrophic gastritis and monitoring of disease activity. However, it should be noted that the diagnosis of chronic atrophic gastritis also requires comprehensive evaluation including clinical symptoms, endoscopic examination, and histopathological examination.
Here we baysen focuse on the diagnostic technology to imporve the quality of life, We have G17/PGI/PGII combo test to sceen the early gastric cancer .
Post time: Apr-03-2024